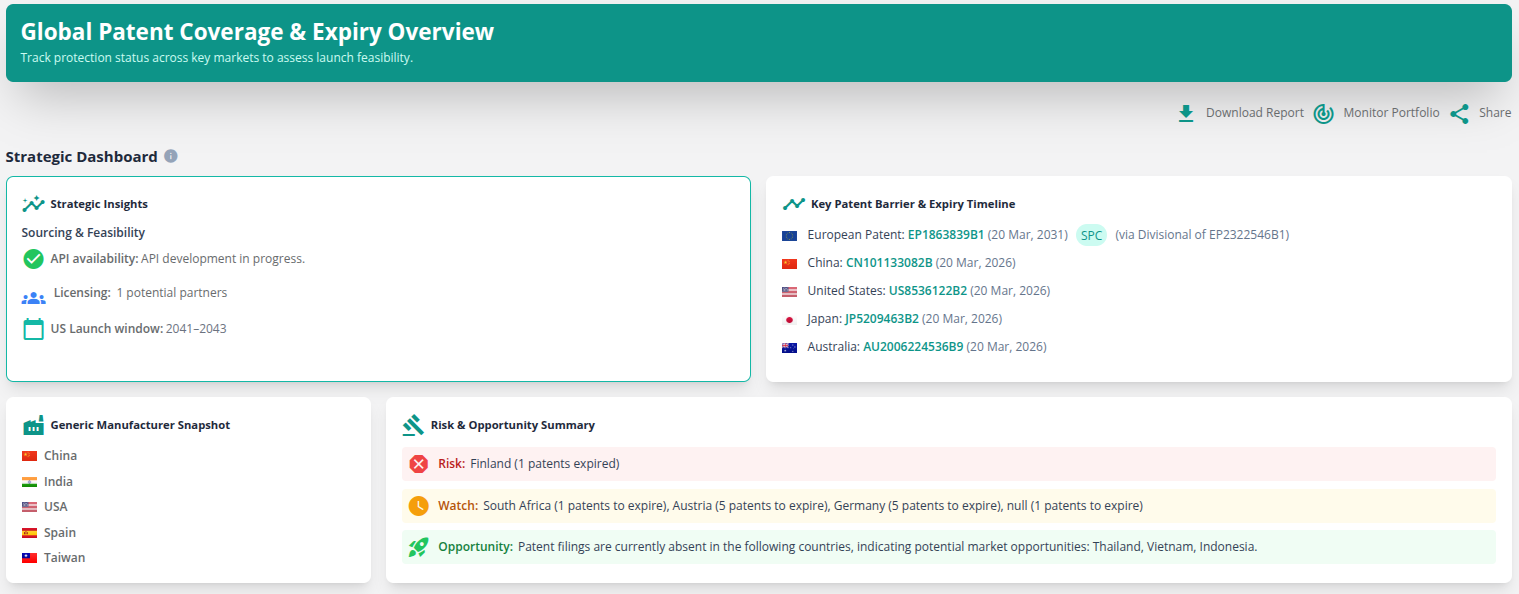
Pirfenidone Patent Expiration
Pirfenidone is used for treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. It was first introduced by Legacy Pharma Inc
Pirfenidone Patents
Given below is the list of patents protecting Pirfenidone, along with the drug name that holds that patent and the company name owning that drug.
| Drug Used in | Drug Patent Number | Drug Patent Title | Drug Patent Expiry | Drug Owner |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esbriet | US10188637 | Granulate formulation of 5-methyl-1-phenyl-2-(1H)-pyridone and method of making the same | Mar 28, 2037 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US8778947 | Methods of administering pirfenidone therapy | Aug 30, 2033 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US7816383 | Methods of administering pirfenidone therapy | Jan 08, 2030 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US7910610 | Methods of administering pirfenidone therapy | Jan 08, 2030 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US8013002 | Methods of administering pirfenidone therapy | Jan 08, 2030 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US8084475 | Pirfenidone therapy and inducers of cytochrome P450 | Jan 08, 2030 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US8318780 | Methods of administering pirfenidone therapy | Jan 08, 2030 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US8648098 | Pirfenidone therapy and inducers of cytochrome P450 | Jan 08, 2030 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US8754109 | Pirfenidone therapy and inducers of cytochrome P450 | Jan 08, 2030 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US7566729 | Modifying pirfenidone treatment for patients with atypical liver function | Apr 22, 2029 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US7635707 | Pirfenidone treatment for patients with atypical liver function | Apr 22, 2029 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US8592462 | Pirfenidone treatment for patients with atypical liver function | Apr 22, 2029 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US8609701 | Pirfenidone treatment for patients with atypical liver function | Apr 22, 2029 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US8383150 | Granulate formulation of pirfenidone and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients | May 10, 2028 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US7696236 | Method of providing pirfenidone therapy to a patient | Dec 18, 2027 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US7696326 | Multiple antigen glycopeptide carbohydrate, vaccine comprising the same and use thereof | Dec 18, 2027 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US7767700 | Method of providing pirfenidone therapy to a patient | Dec 18, 2027 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US8420674 | Method of providing pirfenidone therapy to a patient | Dec 18, 2027 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US7767225 | Capsule formulation of pirfenidone and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients | Sep 22, 2026 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US7988994 | Capsule formulation of pirfenidone and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients | Sep 22, 2026 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US8753679 | Capsule formulation of pirfenidone and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients | Sep 22, 2026 | Legacy Pharma |
| Esbriet | US9561217 | Pharmaceutical composition containing as an active ingredient 5-methyl-1-phenyl-2-(1H)-pyridone |
Jan 25, 2022
(Expired) | Legacy Pharma |
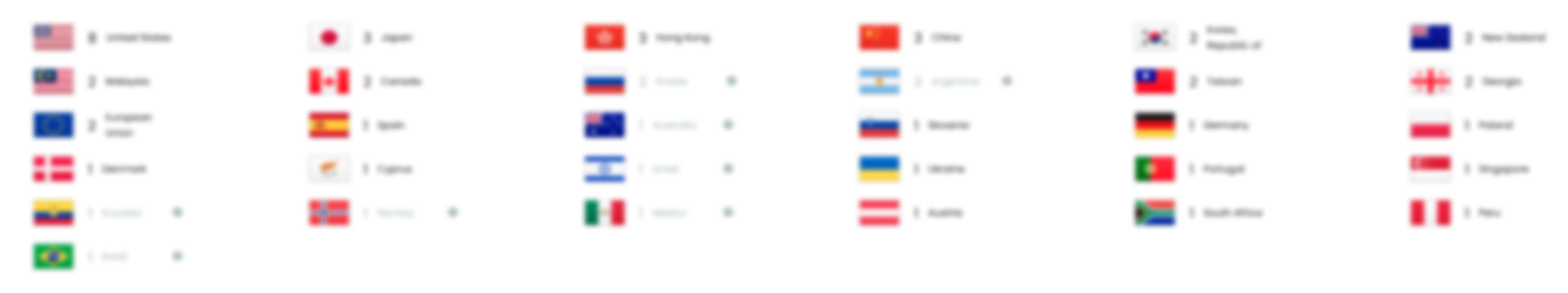
Pirfenidone's Family Patents
Explore Our Curated Drug Screens
Drugs Generating Over $1 Billion in Annual Revenue
Explore the top-performing drugs that dominate the pharmaceutical industry
View List
NCE-1 Patent Expiry in the Next 1 Year
Identify opportunities as new chemical entity (NCE-1) patents approach expiry
View List
Recently Granted Patents in EP
Find the opportunity to file Oppositions
View List